
Before 1901, Australia was not a nation. At that time, the continent consisted of six British colonies which were partly self-governing, but subject to the law-making power of the British Parliament. Each colony had its own government and laws, including its own railway system, postage stamps and tariffs (taxes). This caused a lot of problems and people began to think about the benefits of uniting as one nation, under a federal system of governance.
The path to federation
During the 1890s, each colony sent representatives to special meetings, called conventions, to try to agree about how to form a new federation. Eventually the delegates agreed on the rules for a federal system and a draft constitution. The people of the colonies voted in a series of referendums to accept this new Australian
Constitution. It was then passed as a British Act of Parliament in 1900, called the Commonwealth of Australia Constitution Act, which came into effect on 1 January 1901. The Constitution established a federal Parliament which could make laws on behalf of the new Australian nation (see Australian Constitution).
The colonies of New South Wales, Victoria, Queensland, South Australia and Tasmania united and became states of Australia, known as the Commonwealth of Australia. Western Australia was not a party to the initial agreement but also agreed to join the federation before 1 January 1901.
The territories
In 1901, the two territories did not exist. The Constitution provided for the establishment of a national capital, to be located in New South Wales but at least 100 miles from Sydney. In 1911, the Australian Government created the Australian Capital Territory for this purpose. In the same year, the Northern Territory was also created. Until then, this area had been part of South Australia.
Although part of the Commonwealth, the territories do not have the same legal status as states.
A new nation and a new Parliament
When the Commonwealth of Australia was declared on 1 January 1901, a ceremony was held in Centennial Park in Sydney. The first Governor-General, Lord Hopetoun, was sworn in and the first Prime Minister, Sir Edmund Barton, and federal ministers took the oath of office. Australians celebrated their nationhood, participating in parades, processions, sporting events and school pageants.
The first federal elections for the new Parliament were held on 29 and 30 March 1901. The first Parliament was held in Melbourne on 9 May 1901. It was officially opened by the Duke and Duchess of Cornwall and York (later King George V). The opening ceremony was large and elaborate and further celebrations were held Look at the arches created in Melbourne for the event below.
Can you find information on the other arches?
Australia's federal system
Under the Australian Constitution, the new states united within the Commonwealth. Power was to be shared between the federal Parliament and state parliaments. The federal Parliament would make laws about national matters, such as defence, immigration, trade and the environment.
The power to make and manage federal law would be divided between the Parliament (who would make the law), the Executive (who would put the law into action) and the Judiciary (who would make judgements about the law).
The federal Parliament would be made up of the Queen (represented by the Governor-General), the Senate and the House of Representatives. Laws could only be passed or changed if agreed to by both houses.
The Australian federal system took some of its features from the British Parliament and some from the United States system of governance.












Identify four of the Arches constructed for the visit of the Duke and Duchess of York

Australian Nationalism 1901
Nationalism in Australia is believed to have emerged within the society of emancipists during the early 19th century. It has evolved, and continues to evolve, over time as new events shape Australia's national identity.
Nationalism is defined as a devotion, or sense of loyalty, to one's country.
While the definition of nationalism is relatively straightforward, in reality, the concept of nationalism in Australia is quite complex and ever-changing.
To some people, nationalism is associated with a loyalty to Britain or to both Australia and Britain. There are others, however, who are what historians refer to as radical nationalists. Radical nationalists believe that Australia should become completely independent from Britain.
This distinction between Australian nationalism and British nationalism (union Jack) began to develop during the 19th century in the lead-up to Federation (1901). This transformation was assisted by an increase in the independence of colonial governments, the number of Australian-born subjects and national pride, it was a divided nation.
Federation consolidated feelings of nationalism among the Australian people.
Nationalism, however, has sometimes encouraged people to think that their country is superior to another country. This was particularly evident around the time of Federation.
Part of the reason that the colonies supported Federation was out of fear of being invaded by non-white immigrants. Despite the fact that several colonies already had implemented laws which restricted immigrants from certain countries, all of the colonies were keen to strengthen their immigration policies by uniting to keep non-whites out of Australia.
The first Australian Federal Parliament was opened on 13 May and it did not waste any time in fulfilling its pre-Federation intentions. As a consequence of racist views of white-superiority, and fears of non-whites taking white workers' jobs lowering wages and working conditions, the federal government passed the Immigration Restriction Act 1901, and the Pacific Island Laborers Act 1901.
These two pieces of legislation
marked the beginning of the
White Australia policy



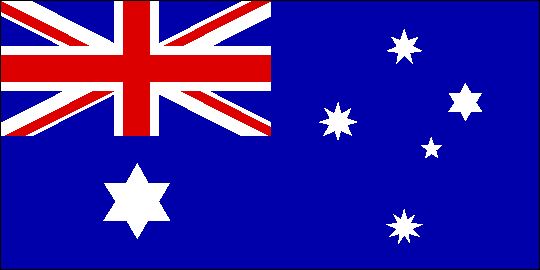
Can you spot the difference between this Flag and the one above?
Can you explain the difference?

History Lessons:
Time capsule
Prepare your workbooks and Download the Pdf below, open and read it from page one to the begining of object one. As we will not be printing this document, you will need to prepare tables and list responses to questions in the pdf worksheet, into your workbooks.
In todays lesson we will be taking a closer look at Federation.
You will be required to research the information provided and report in note format...
-
what federation means to Australia.
-
the chronology (timeline) of events that lead to Federation.
You can then write an informative piece (in notated format) upon either,
one charcter who contributed to this event, explaining what their contribution and interest was,
explore and describe the lead up to Federation starting with the 1889 federation conventions.
Or choose a specific event in the chronology to look at and explain indepth.
.


